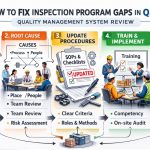
Preparing For FDA QMSR Inspection Program Audit
The transition to the Quality Management System Regulation (QMSR) marks a significant evolution in how the FDA oversees medical device manufacturing. For organizations, preparing for an FDA QMSR inspection program audit is no longer just about following 21 CFR 820; it is about harmonizing with ISO 13485:2016. This shift demands a more integrated, risk-based approach to quality. To succeed, companies must overhaul their internal audit processes and ensure that every layer of their organization is aligned with the new expectations.
A successful audit begins with a proactive mindset. Instead of waiting for an inspector to arrive, leading firms are already conducting deep-dive gap analyses. By understanding the FDA QMSR Inspection Program Rule Interpretation, manufacturers can identify where their legacy systems might fall short. The focus has moved from mere documentation to the actual effectiveness of the quality system in ensuring device safety and efficacy.
The Core of QMSR Readiness
At the heart of the new regulation is the integration of risk management into all aspects of the QMS. During an audit, inspectors will look for evidence that risk isn’t just a file in a folder, but a living part of the production and design process. Utilizing a Medical Device QMSR Inspection Program Template can help standardize your internal checks, ensuring that no critical area is overlooked. This structured approach is essential for maintaining consistency across multiple manufacturing sites.
Navigating Modern Compliance Challenges
The road to compliance is often paved with technical hurdles. Common QMSR Inspection Program Challenges For Medtech include legacy data migration, staff retraining, and the synchronization of disparate quality processes. Many companies find that their old “check-the-box” mentality does not hold up under the rigorous process-oriented scrutiny of a QMSR audit. Inspectors now prioritize how processes interact and how management reviews impact overall quality outcomes.
To overcome these obstacles, an Introduction to QMSR Compliance Best Practices is vital for your quality team. This involves shifting from a reactive “correction” mode to a proactive “prevention” strategy. When you treat the audit as a tool for improvement rather than a hurdle to clear, the technical gaps become much easier to identify and close. Training your internal auditors to think like FDA investigators is one of the most effective ways to ensure readiness.
Strategic Implementation of Quality Controls
Implementing Best Practices For Medical Device Inspection Program QMSR Compliance requires more than just updated SOPs. It requires a cultural shift where quality is seen as everyone’s responsibility. High-performing companies use cross-functional teams to review audit findings, ensuring that insights from the manufacturing floor reach the design engineers and senior management. This closed-loop system is exactly what the FDA looks for during a QMSR evaluation.
Leveraging Technology for Audit Success
In the digital age, manual systems are a liability. The Top inspection Program Tools For QMSR Compliance allow for real-time tracking of quality metrics, making it much easier to demonstrate control to an auditor. These tools provide a “single source of truth,” reducing the risk of conflicting data and ensuring that all electronic records meet the stringent requirements of 21 CFR Part 11.
Modern audit software can:
- Automate the scheduling of internal inspections.
- Track CAPA effectiveness in real-time.
- Provide instant access to validation documents.
- Facilitate remote audits through secure cloud portals.
Data Integrity and Documentation
One of the most common reasons for audit failure is poor data integrity. Under QMSR, the “ALCOA” principles (Attributable, Legible, Contemporaneous, Original, and Accurate) are more important than ever. Your documentation must tell a clear story of how a product was made and why certain decisions were made. If an auditor cannot follow the trail of a non-conformance from detection to resolution, they will likely issue a 483 observation.
Technical Depth: Risk-Based Auditing
The QMSR framework emphasizes a “Process Approach.” This means auditors will follow a process from start to finish, looking at inputs, resources, activities, and outputs. For example, when auditing design controls, they won’t just look at the design plan; they will look at how human factors and risk assessments influenced the final product specifications. To prepare, your internal audit team should conduct “stress tests” on high-risk processes to see if the existing controls are truly robust.
Furthermore, management responsibility has been elevated. Auditors will expect to see that senior leadership is actively involved in quality issues. This isn’t just about signing off on reports; it’s about demonstrating that quality metrics drive business decisions. If there is a disconnect between the production goals and quality standards, it is a major red flag for any FDA inspector.
Finalizing Your Audit Readiness Plan
As you finalize your preparation, conduct a “Mock FDA Audit.” This exercise should be as realistic as possible, involving “front room” and “back room” teams to practice document retrieval and interview techniques. Use the findings from this mock audit to refine your processes and build confidence among your staff. Remember, the goal of the QMSR is to ensure that every medical device reaching a patient is safe, effective, and manufactured to the highest standards.
By aligning your internal inspection program with international standards and leveraging modern technology, you can turn the challenge of a QMSR audit into an opportunity for operational excellence. Continuous monitoring and a commitment to data-driven quality will ensure that your organization remains compliant and competitive in the evolving global medtech market.
FAQs
1. How long do I have to transition from QSR to QMSR? The FDA provided a transition period, but by 2026, most manufacturers are expected to be fully aligned with QMSR. It is critical to check the latest FDA guidance for specific deadlines.
2. Is ISO 13485:2016 certification enough for QMSR compliance? While QMSR is heavily based on ISO 13485, the FDA still maintains specific requirements (like 21 CFR Part 4 for combination products). You must ensure your system covers both the ISO standard and the FDA’s unique additions.
3. What are the most common findings in a QMSR audit? Early trends suggest that inadequate risk management integration and poor management review documentation are the top areas for findings.
4. How does the FDA handle remote audits under QMSR? The FDA has increased its use of Remote Regulatory Assessments (RRAs). Ensuring your digital files are organized and accessible via secure platforms is key to a smooth remote audit.
5. Do I need to re-validate my QMS software for QMSR? If the transition changes how you use the software or if you are implementing new modules to meet QMSR requirements, a validation assessment is mandatory.
6. What role does the “Internal Audit” play in the official FDA inspection? The FDA usually does not review your actual internal audit reports to encourage honest self-assessment, but they will check if the audits were performed and if the resulting CAPAs were effective.
References
- FDA QMSR Final Rule Documentation: https://www.federalregister.gov – The foundational legal document outlining the requirements for the new Quality Management System Regulation.
- ISO 13485:2016 Quality Management Systems: https://www.iso.org – The international standard that serves as the basis for QMSR compliance for medical devices.
- FDA Inspection References and Manuals: https://www.fda.gov – Official guides used by FDA investigators to conduct inspections of medical device manufacturers.
- Medical Device Innovation Consortium (MDIC) Case for Quality: https://mdic.org – Resources and whitepapers on shifting from compliance to quality-driven manufacturing.
- Global Harmonization Working Party (GHWP) Resources: https://www.ghwp.info – Provides guidance on the international alignment of regulatory requirements and audit practices.
- RAPS Regulatory Focus Analysis: https://www.raps.org – Expert commentary on the practical implications of QMSR for medtech professionals.