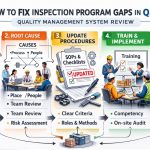
Introduction to QMSR Inspection Challenges in MedTech
The regulatory landscape for the MedTech sector is shifting rapidly. Recently, the FDA finalized the Quality Management System Regulation (QMSR). This represents a fundamental change in industry oversight. Consequently, manufacturers now face unique QMSR inspection challenges that did not exist before. This evolution requires moving from static paperwork to a dynamic quality culture. As we move through 2026, firms must recognize that investigators now focus on process effectiveness rather than just procedural adherence.
For many organizations, the primary hurdle is reconciling legacy systems with new integrated requirements. The FDA now expects to see risk management woven into every production stage. Therefore, understanding these obstacles is vital for maintaining market access. Failure to address systemic gaps often leads to avoidable 483 observations and costly interventions. In the following sections, we explore frequent pitfalls and provide strategies to overcome them. By adopting a proactive mindset, your firm can transform these challenges into opportunities for operational excellence.
In this guide, we break down the core components of the new program. We also discuss how digitalization impacts compliance. Finally, we provide a roadmap for maintaining an audit-ready state. Whether you lead a startup or a global firm, you must master these requirements to navigate the modern FDA landscape.
The Gap Between Legacy QSR and New QMSR Requirements
One persistent challenge involves the actual interpretation of the new rule. Many firms mistakenly believe that ISO 13485 certification automatically guarantees FDA compliance. However, the FDA QMSR Inspection Program Rule Interpretation reveals specific statutory requirements beyond the international standard. This gap creates a significant risk for manufacturers who fail to map their processes correctly.
Investigators specifically look for updated quality manuals that reflect the harmonization. If your documentation still relies on old QSR terminology, it signals a lack of readiness. Furthermore, the transition requires a deep dive into historical data. You must ensure that legacy risk assessments meet current expectations. To manage this effectively, many organizations use a Medical Device QMSR Inspection Program Template to standardize their efforts. This structured approach helps ensure no regulatory requirement is overlooked during the shift.
Integrating Risk Management Across the Lifecycle
Risk management serves as the centerpiece of the QMSR framework. Traditionally, MedTech firms treated risk as a standalone activity in the design phase. Under the new regulation, however, risk must inform purchasing, production, and post-market surveillance. This integration is one of the most difficult QMSR inspection challenges to solve. Investigators will look for a “risk thread” that connects every operational subsystem.
For example, if a supplier changes a raw material, the FDA expects a documented risk assessment. You must prove how that change impacts the finished device. If this link is missing, it constitutes a major non-compliance. Therefore, firms must learn How to Implement Medical Device Inspection Program QMSR strategies that emphasize data sharing. When risk management becomes a living part of the QMS, it provides a robust defense against scrutiny. This proactive approach ensures patient safety remains the primary driver of every decision.
Data Integrity and the Pitfalls of Digitalization
As manufacturing becomes more automated, data integrity has emerged as a high-priority focus. The challenges in this area often stem from a lack of software validation. The FDA requires that any digital system used in the QMS must be fully validated. If your audit trails are incomplete or your signatures do not meet Part 11 requirements, your quality record is at risk.
Investigators in 2026 are trained to look for unauthorized data manipulation. They want to see that your digital systems support the ALCOA+ principles. Consequently, manufacturers must ensure their IT infrastructure is as compliant as their production floor. This requires regular system audits and unalterable time-stamped records. By prioritizing digital integrity, you protect the veracity of your data. You also demonstrate high regulatory maturity to the federal investigator.
Operational Hurdles in Audit Readiness
Maintaining a state of “continuous readiness” is a significant operational challenge. Many firms still rely on the “panic-prep” model. However, this is no longer effective under the QMSR. To succeed, organizations must adopt a Step-by-Step Medical Device Inspection Program for QMSR Compliance. This program should include frequent internal audits that test both technical data and staff competency.
One common operational challenge involves “Back Room” logistics. During an audit, document retrieval speed indicates organizational control. If your team cannot provide a requested report within minutes, it creates a negative impression. Therefore, practicing document retrieval and SME interviewing is essential. Your staff must be able to articulate the “why” behind their quality actions. This level of preparation transforms an inspection from a stressful event into a routine verification of excellence.
The High Cost of Inadequate CAPA Investigations
Corrective and Preventive Action (CAPA) remains the most cited area for 483 observations. In the QMSR era, the FDA expects a more holistic and risk-centric approach. Investigators are moving away from “band-aid” fixes toward deep root cause analysis. A common challenge is failing to link CAPA activities to the broader risk management file. If a recurring failure does not update your risk assessments, you are not truly compliant.
To safeguard your system, you should use a comprehensive QMSR Inspection Program Checklist for Medical Devices. This checklist should verify that every investigation considers the impact on the overall risk profile. Furthermore, the FDA seeks evidence of “Effectiveness Checks.” You must prove that your actions actually worked and did not introduce new risks. Transparency in your investigation process is the best way to satisfy investigator curiosity.
QMSR vs ISO 13485: Understanding the Nuances
Manufacturers often struggle with the subtle differences between these two frameworks. While the QMSR incorporates the international standard, the FDA retains specific legal authority. Consequently, a QMS that passes an ISO audit might still fail an FDA inspection. This is one of the most confusing QMSR inspection challenges for global firms.
Understanding the QMSR vs ISO 13485 Inspection Program Differences is critical for strategic planning. The FDA focuses more on public health safety and statutory reporting than a typical registrar. For instance, the FDA’s Medical Device Reporting (MDR) requirements are much more prescriptive. Your internal audit program must account for these additional layers to ensure total compliance.
Conclusion: Navigating the Future of QMSR Compliance
The road to QMSR compliance is paved with significant challenges. However, it also offers a clear path toward better product quality. By addressing these challenges today, MedTech firms can ensure a smooth transition. The key is to embrace risk-based thinking and prioritize data integrity. Move toward a culture of continuous audit readiness.
Regulatory compliance should be a strategic investment rather than a burden. Firms that harmonize their processes with the new FDA guidance will be better positioned globally. Stay proactive and use the tools available. Ensure your QMS is resilient enough for the modern investigative landscape. By doing so, you protect your brand, your patients, and your future.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the most cited QMSR inspection challenge? The most frequent challenge is failing to integrate risk management across all subsystems, particularly in purchasing and production controls.
2. How does the QMSR affect legacy 21 CFR 820 systems? Manufacturers must update their procedures to include ISO 13485 terminology and more explicit risk-based requirements.
3. Does the FDA require software validation for all digital tools? Yes, any software used in the QMS or manufacturing process must be validated to ensure data integrity under 21 CFR Part 11.
4. How often should a MedTech firm conduct a mock audit? Industry best practice is to conduct a full mock audit every 12 to 18 months, with focused “mini-audits” performed quarterly.
5. What is the biggest difference between ISO and QMSR inspections? The FDA investigator focuses on legal compliance and public health safety, while ISO auditors focus on standard conformity.
6. Can a MedTech firm use eQMS software to overcome these gaps? Yes, a validated eQMS can automate document control and CAPA, significantly reducing the risk of human error.
References and Technical Citations
FDA QMSR Final Rule (2026): https://www.fda.gov/medical-devices/quality-system-regulation-amendment The official regulation detailing the mandatory transition and the integration of ISO 13485:2016 into US law.
ISO 13485:2016 – Quality Management Systems Standard: https://www.iso.org/standard/59752.html The primary international standard serving as the foundation for the new FDA QMSR framework.
FDA Inspection Guides – QSIT Methodology: https://www.fda.gov/inspections-guides/qsit A technical guide outlining how federal investigators evaluate the effectiveness of a quality management system.
FDA Data Integrity Guidance Documents: https://www.fda.gov/regulatory-information/data-integrity-compliance Critical guidance for manufacturers to ensure records meet necessary standards for accuracy and security.
IMDRF – Software Validation Principles: https://www.imdrf.org/documents/software-validation-samd The international framework for validating software in the medical device sector, essential for QMSR goals.
FDA Guidance on MDR Requirements: https://www.fda.gov/medical-devices/postmarket-requirements/mdr Technical details on the mandatory reporting of device malfunctions, which remains a key part of QMSR inspections.