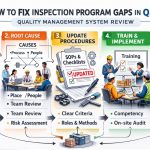
Outsourced vs Internal QMSR Inspection Program Pros and Cons
The medical device industry is currently witnessing a historic shift with the FDA’s transition from the Quality System Regulation (QSR) to the Quality Management System Regulation (QMSR). This harmonization with ISO 13485:2016 means that manufacturers must re-evaluate their audit and inspection strategies. A central question arises: Should you maintain an internal QMSR inspection program, or is it more efficient to outsource this critical function to third-party experts?
Choosing between these two models is not merely a financial decision; it is a strategic move that affects your long-term FDA compliance and product safety. An internal program offers direct control and deep institutional knowledge, while an outsourced model provides objective neutrality and specialized regulatory expertise. Both paths have distinct advantages and challenges that can significantly influence your success during a formal FDA inspection.
Before diving into the detailed comparison, it is essential to understand the foundational requirements. For those looking to align their current processes, exploring an FDA QMSR Inspection Program Rule Interpretation can provide the necessary context for why these inspections are becoming more rigorous.
The Rise of the QMSR Framework
The QMSR framework emphasizes risk management and document control more than its predecessor. As the FDA begins enforcing these standards, the complexity of internal audits has increased. Organizations now need to decide if their internal teams have the bandwidth to stay updated with evolving 2025 FDA trends or if external consultants are necessary to bridge the gap.
Internal QMSR Inspection Programs: The Pros
An internal QMSR inspection program is built within the organization’s own quality department. The primary benefit is Institutional Knowledge. Internal auditors understand the nuances of the manufacturing floor, the history of CAPA (Corrective and Preventive Actions), and the specific culture of the company.
- Cost-Efficiency over Time: While training staff is expensive, a mature internal team can perform frequent “spot checks” without the recurring high fees of external consultants.
- Immediate Feedback Loops: Internal teams can identify a deviation and initiate a CAPA System process immediately without waiting for a scheduled consultant visit.
- Cultural Integration: Compliance becomes a part of the daily routine rather than a “scary event” triggered by an outsider’s arrival.
For companies starting from scratch, utilizing a Medical Device QMSR Inspection Program Template can help in structuring these internal efforts effectively.
Internal QMSR Inspection Programs: The Cons
However, internal programs often suffer from “Tunnel Vision.” When staff members audit their own colleagues or processes they helped design, objectivity can take a backseat.
- Resource Drain: Small to mid-sized firms often find that their best engineers are tied up in auditing rather than innovating.
- Skill Gaps: Keeping up with the latest regulatory updates requires constant training, which many companies fail to prioritize.
- Lack of Authority: Sometimes, internal findings are not taken as seriously by upper management as those delivered by a high-priced external firm.
Outsourced QMSR Inspection Programs: The Pros
Outsourcing the inspection program involves hiring specialized firms to conduct gap analyses and mock audits. The most significant advantage here is Objective Neutrality.
- Expertise and Specialization: Consultants often consist of former FDA investigators who know exactly what a real inspector will look for. They bring a fresh set of eyes to data integrity issues that internal teams might overlook.
- Scalability: You can scale the intensity of inspections based on your product development cycle.
- Benchmarking: External auditors can tell you how your Quality Management System stacks up against industry peers.
Many firms find that learning How to Implement Medical Device Inspection Program QMSR is much faster when guided by an experienced third party.
Outsourced QMSR Inspection Programs: The Cons
The most obvious drawback is Cost. High-level regulatory consulting is expensive. Additionally, there is a risk of “knowledge leakage” where the consultant identifies problems but the internal team doesn’t truly learn how to prevent them in the future.
- Scheduling Conflicts: You are at the mercy of the consultant’s availability.
- Surface-Level Understanding: A consultant might miss deep-rooted cultural issues that only an insider would see.
Step-by-Step Implementation for Compliance
Regardless of the chosen model, the implementation must be methodical. A Step-by-Step Medical Device Inspection Program for QMSR Compliance ensures that no stone is left unturned. This includes:
- Gap Analysis against ISO 13485:2016.
- Updating SOPs to reflect QMSR language.
- Training staff on the new risk-based approach.
- Conducting a full-scale mock audit.
To stay organized, many managers rely on a QMSR Inspection Program Checklist for Medical Devices to track progress across various departments, from design controls to post-market surveillance.
Do You Need a Mock FDA Audit?
One of the most effective uses of an outsourced program is the “Mock Audit.” This is a simulated inspection that mimics the pressure and scrutiny of a real FDA visit. Understanding the Benefits and What to Expect from a Mock FDA Audit can be the difference between a clean report and receiving a dreaded FDA Warning Letter.
Mock audits provide a “safe” environment to fail. They reveal weaknesses in your medical device compliance strategy without the legal or financial repercussions of an official 483 observation.
| Feature | Internal Program | Outsourced Program |
| Initial Cost | Moderate (Training/Staff) | High (Consulting Fees) |
| Long-term Cost | Low | High |
| Objectivity | Low to Moderate | Very High |
| Institutional Knowledge | Very High | Low |
| Compliance Risk | Moderate (Bias Risk) | Low (Expert View) |
Strategic Recommendation
For most mid-sized medical device manufacturers, a Hybrid Model is the most effective approach. Maintain a core internal team for monthly self-assessments and bring in an outsourced expert once or twice a year for a high-level GxP Audit. This ensures you have both the daily oversight and the periodic “reality check” needed to maintain Pharmaceutical Quality and regulatory alignment.
Conclusion
The transition to QMSR is a journey, not a destination. Whether you choose an internal, outsourced, or hybrid inspection program, the goal remains the same: ensuring that your Quality Management System is robust enough to protect patient safety and withstand regulatory scrutiny. By weighing the pros and cons of each model, you can build a program that not only satisfies the FDA but also improves your overall operational excellence.
FAQs
1. What is the biggest difference between QSR and QMSR during inspections? The biggest difference lies in the integration of ISO 13485:2016. The FDA now places a much heavier emphasis on risk management throughout the entire product lifecycle, whereas the old QSR was more focused on specific manufacturing controls.
2. Can I rely solely on internal audits for FDA readiness? While legally permissible, it is risky. Internal audits often miss systemic issues due to familiarity. A periodic external check is highly recommended to ensure FDA Inspection Readiness.
3. How often should QMSR inspections be conducted? At a minimum, a full system audit should be performed annually. However, high-risk areas like Sterilization or Software Validation may require more frequent quarterly checks.
4. Are outsourced auditors allowed to speak with the FDA on our behalf? During a real inspection, consultants can act as “back-room” support, but the FDA requires the company’s own employees to answer the investigator’s questions directly.
5. What is the cost of a typical outsourced QMSR mock audit? Costs vary depending on the size of the facility and scope, but typically range from $10,000 to $50,000 for a comprehensive 3-5 day inspection.
6. Does the QMSR apply to foreign manufacturers? Yes, any manufacturer selling medical devices in the US market must comply with QMSR, regardless of their physical location.
References & Citations
- FDA QMSR Final Rule: The official regulation detailing the transition and harmonization with ISO 13485. View Source
- ISO 13485:2016 Standard: The international standard for medical device quality management systems which forms the basis of QMSR. View Source
- Medical Device Directive (MDD) vs QMSR: A comparative study on how global regulations are aligning toward a single quality standard. View Source
- Journal of Regulatory Compliance: An article discussing the statistical success rates of companies using outsourced vs internal audit teams. View Source
- Rethinking Internal Audits: A whitepaper on how to remove bias from internal quality inspection programs in the life sciences. View Source